 Are you or someone you know living with eczema? Eczema, otherwise known as atopic dermatitis, is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that affects millions of people of all ages worldwide. While there is no known cure, there are treatment options and lifestyle changes that can help manage symptoms. In this blog post, we will explore who is affected by eczema and what you need to know to manage this condition.
Are you or someone you know living with eczema? Eczema, otherwise known as atopic dermatitis, is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that affects millions of people of all ages worldwide. While there is no known cure, there are treatment options and lifestyle changes that can help manage symptoms. In this blog post, we will explore who is affected by eczema and what you need to know to manage this condition.
Children and Infants:
Eczema is common in children and infants, affecting around 10-20% of infants and 3% of children and adults in the United States. It can start as early as 2-3 months old and may improve as the child gets older, although some people may experience eczema throughout their lives. In infants, eczema most commonly appears on the face, scalp, and outer arms and legs, while in children, it often appears on the inside of the elbows and behind the knees.
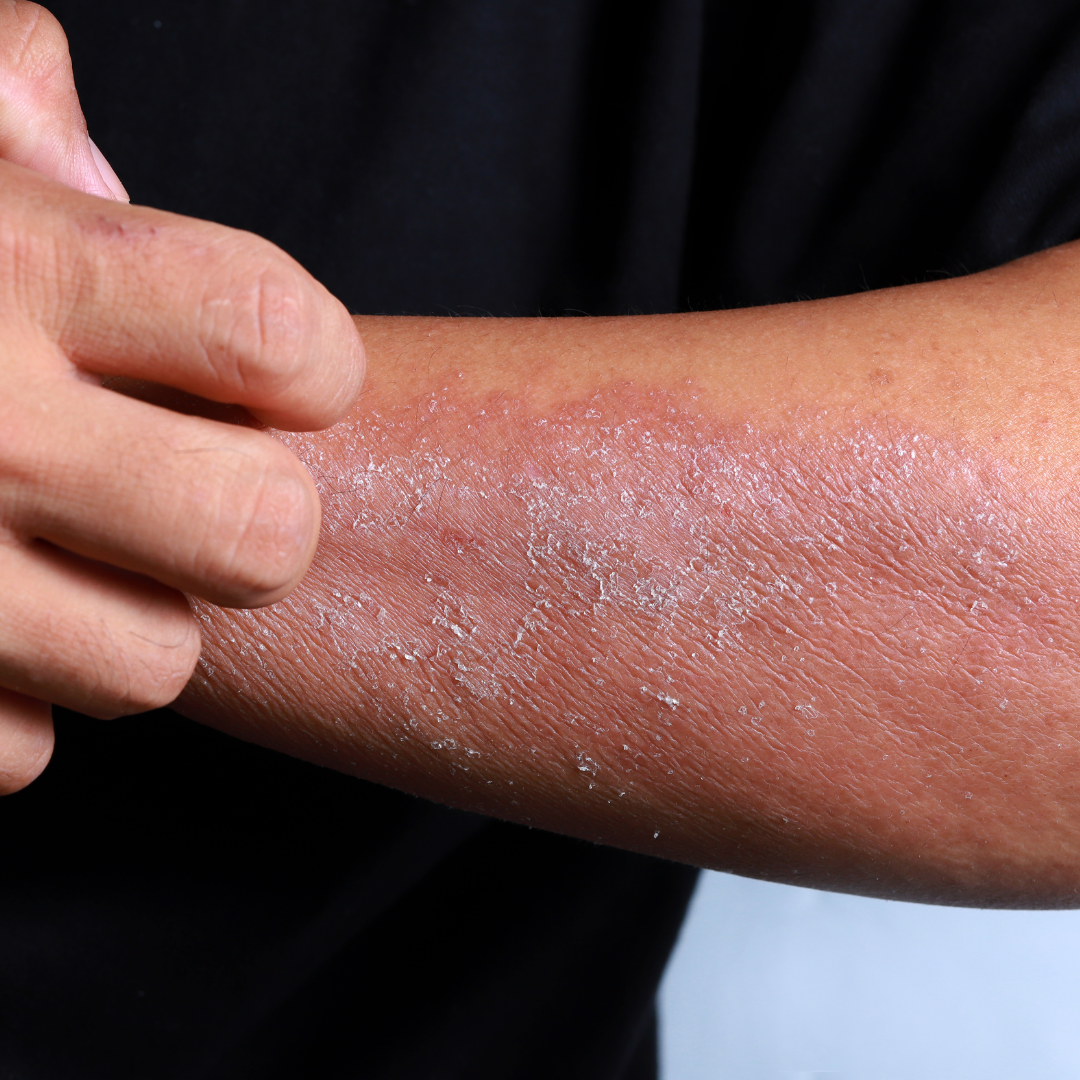
Adults:
Eczema is not just a childhood condition, as it can affect individuals of all ages. In adults, it often appears on the hands, arms, and legs, and can be triggered by stress, allergies, or irritants. It is estimated that around 10% of adults in the United States have eczema, and it can be especially challenging to manage as it can affect daily activities and impact quality of life.
Individuals with Allergies or Asthma:
If you or someone in your family has allergies or asthma, you may be more likely to develop eczema. There is a genetic link between these conditions, and they can often occur together. Allergies can aggravate eczema symptoms, and managing allergies can be an important part of managing eczema.
Those with Compromised Skin Barrier:
Eczema is often associated with a weakened skin barrier, making it easier for irritants and allergens to penetrate the skin and trigger symptoms. Those with dry skin, frequent hand washing, or who work in jobs that require frequent hand washing or exposure to irritants are more likely to develop eczema. It is important to keep the skin moisturized and avoid triggers to reduce symptoms.
People of Color:
While eczema can affect people of all skin types, it may look different on those with darker skin tones. In people of color, eczema may appear as patches of dark or light skin, or scaly patches that may be mistaken for other skin conditions. It is important to receive a proper diagnosis from a healthcare professional to ensure effective treatment.
Skin Care:
People with eczema can benefit from gentle skin care. Limiting showers & baths to once daily (if needed), short in time, lukewarm water, and using a gentle cleanser. There is no need to use loofahs or washcloths. When you get out, pat dry, and within 2-3 minutes, apply a moisturizer such as a cream or ointment. Look for ingredients like ceramides to help replenish the skin barrier. Apply moisturizers twice a day and throughout the day after washing hands or getting out of the water. Use fragrance-free detergents. Consistency is key when it comes to treating eczema.
Eczema can be a challenging condition to manage, but understanding who is affected and the triggers that can worsen symptoms can make a significant difference in symptom control. If you or someone you know is living with eczema, consult with a healthcare professional to develop a personalized treatment plan that may include lifestyle changes, gentle skin care, trigger avoidance, allergy management, and topical & systemic medications. With proper care and attention, individuals can manage their symptoms and live a comfortable life.
About the Author

Meet Dr. Katharine Saussy, an accomplished dermatologist and a proud native of New Orleans. Dr. Saussy is a member of the American Academy of Dermatology and Women’s Dermatologic Society, with expertise in medical, pediatric, surgical, cosmetic, and skincare. Her strong passion for sun safety is reflected in her practice, where she provides exceptional care to patients of all ages.
